Leaving Cert Biology Revision: Human Reproduction
- Javeria Saleem
- Jun 10, 2024
- 6 min read
Human Reproduction
Men and women alike have,
One pair of structures that result in gametes, or meiotic sex cells.
A set of transportable tubes.
Several glands release hormones that regulate fertility.

Male Reproductive System
Testes
The 50-centimeter tubules in the male gonads create sperm, while the cells that lie between them make testosterone.
Epididymis
are matured and stored for six weeks in the epididymis.
Sperm duct
Sperm go via the sperm duct to the urethra.
Urethra
Urine and semen are expelled from the penis through the urethra.
Sperm nourishment (fructose) and swimming ability are provided by seminal vesicles, the
prostate, and Cowper's gland.
Semen is the collective term for the fluid and sperm.
The Male Reproductive System's Hormones
The hormone FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone brings testicular meiosis on.
The testes produce testosterone because of the action of the L.H. Luteinizing Hormone.
The primary male hormone is testosterone (Androgen). causes the development of male genitalia in the womb and the subsequent puberty of secondary traits.

Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Aside from the actual sex organs, these characteristics make males and females unique.
The development of pubic, underarm, and chest hair.
Deeper voice because of larynx enlargement.
The growth of muscles and bones.
A spike in growth and broadening of the shoulders.
The skin has more sebum, or oil, which results in spots.
Male Infertility
The incapacity to bear children is known as infertility.
Male infertility is primarily caused by a low sperm count. It is brought on by hormones, alcohol consumption, tobacco use, and drug use. Stop all the following treatments and start taking hormone supplements.
Low sperm motility (poor swimmers) is another factor.
Failure of the endocrine gland (hormone).
Enzymes from the acrosome are consumed by the egg. The X or Y chromosome is found in the nucleus. Numerous mitochondria in the collar power the tail.
Female Reproductive System
Female gonads in the ovaries generate hormones and eggs. During puberty, meiosis produces 20 eggs every month. Usually, just one makes it.
A Graafian follicle that produces the female hormone estrogen surrounds the egg (ovum). During ovulation, this follicle ruptures, releasing the egg.
The follicle that becomes the corpus luteum fills with yellow fluids after ovulation. Progesterone is produced because of this. The oviduct, also referred to as the Fallopian tube, transports the egg to the womb.
The uterus, often known as the womb, is a muscular organ that houses the endometrium, which supplies nutrition to the growing embryo. The vagina is a muscular tube via which sperm can enter and babies can escape.

The Menstrual Cycle
Days 1- 5
The old uterine lining decomposes and is expelled.
We refer to this as menstruation. A fresh egg is created during meiosis and is encased in a Graafian follicle.
Days 6 - 14
Estrogen is produced by the Graafian follicle, thickening the lining of the womb and preventing the production of additional eggs.
Day 14: The egg travels into one of the Fallopian tubes when the Graafian follicle ruptures. It lasts for roughly 48 hours.
Day 14 - 28: Progesterone is released by the Corpus Leutum, which develops from the Graafian follicle. As a result, the lining of the womb tightens and no more eggs are generated.
The Female Reproductive System's Hormones
Adjacent Sexual Features
During the first 14 days of pregnancy, estrogen thickens the lining of the womb. For the next fourteen days, progesterone keeps the lining of the womb thicker. Both are present in the contraceptive pill and prevent the development of eggs.
Other than the actual sex organs, these characteristics make males and females unique.
1. The pubic and underarm hair growth.
2. Breasts develop and grow larger.
3. A rise in body fat.
4. The rectum widens during childbirth.
5. Adrenal gland testosterone causes a growth surge.
Infertility in Women
The incapacity to bear children is known as infertility. The primary cause of infertility in females is failure to ovulate. It is brought on by endocrine gland dysfunction. Eggs may not develop or be released if FSH or LH are either not produced at all or are produced in excess.
Supplemental hormones are administered for treatment.
IVF, or in vitro fertilization, is a procedure done when a man's sperm count is low, hormones prevent ovulation, or the fallopian tubes are blocked.
During the first two weeks after using fertility medication, females generate several eggs.
After being extracted, the eggs and sperm are combined in a dish (in vitro). Any remaining embryos are reinserted into the womb after two days.
This usually allows a woman to give birth to several children.
Menstrual Cycle Hormones (Only Higher Levels)
1. The pituitary gland produces FSH, which increases egg production, starting on days 1-5.
2. Day 5-14 Graafian follicles release estrogen, which thickens the lining of the womb, inhibits the development of FSH (which blocks the formation of additional eggs), and causes the production of LH.
3. On day 14, the pituitary gland produces LH, which triggers ovulation, maintains the lining of the womb, and transforms the Graafian follicle into the corpus luteum. Finally, progesterone, the last hormone, is produced by the corpus luteum.
4. Starting on days 14-28, the pituitary gland produces progesterone, which inhibits both FSH and LH and halts any uterine contractions. In the event of no pregnancy, the corpus luteum decomposes by day 22. By day 28, the uterus contracts, the lining ruptures, and FSH is released once more because of low progesterone and estrogen levels.
Disorders of the Menstrual Cycle fibroids
Benign cancerous growths in the womb are called fibroids. They vary in size from grapefruit to pea. They may bleed, hurt, and interfere with fertility. Treatment: surgical excision of the womb, if it is too large.
The Stages of Copulation
Five minutes after insemination, contractions might transfer sperm into the fallopian tubes.
They locate the egg by chemotaxis, which uses a chemical scent. Numerous sperm will encounter resistance from white blood cells, mis-route, or sense an excessively acidic vagina.
Fertilisation
In females, sperm can live for up to four days. The egg has a two-day shelf life. In the fallopian tube, fertilization takes place if sexual activity takes place between Day 7-18. After fertilization, 6-9 days later, implantation takes place.
The embryo connects to the lining of the uterus at this point. The embryo is shielded from harm by the amniotic fluid and the membrane that surrounds it.

The Placenta
The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy. It provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing baby and removes waste products from the baby's blood.
The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus, and the baby's umbilical cord arises from it.
This vital organ ensures the baby receives everything needed to grow and develop while in the womb.
Zygote Development
Fertilization starts on Day 1.
Day 3 Zygote grows by mitosis becoming a morula.
Day 5: Develops into a hollow ball known as a blastocyst.
The uterus is now involved in this.
Day 10: Three germ layers form.
Growth up to 8 Weeks
The heart develops and begins to beat at four weeks. The neural cord and brain develop.
The internal organs and limbs form by week five. The lips, ears, nose, and eyes are visible for six weeks.
By week 8, the majority of the organs have formed, and the tail has shrunk. Known as a fetus now.
Stages of Birth
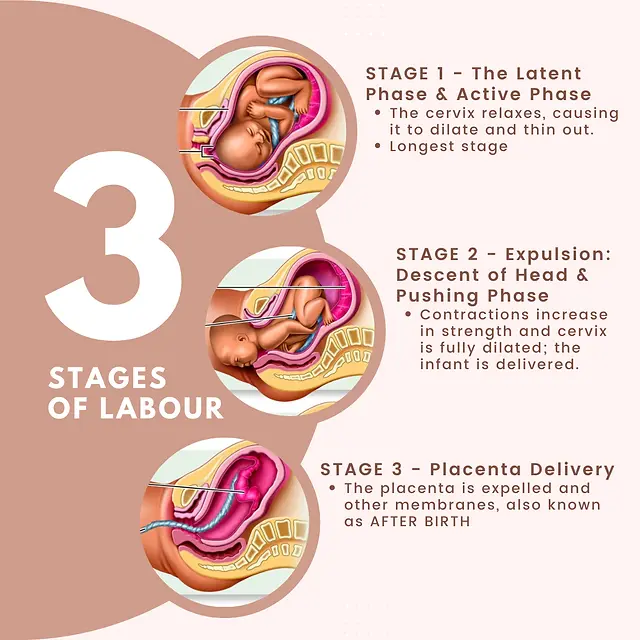
Breastfeeding
The thick golden liquid known as colostrum appears before milk. is rich in proteins, minerals, and antibodies.
The thick golden liquid called colostrum precedes milk.
Has many proteins, minerals, and antibodies.
Until the infant quite nursing, prolactin stimulates the production of milk.
Benefits of Breastfeeding
The milk contains the ideal balance of nutrients needed by the baby.
Contains antibodies from the mother for most common diseases.
Safer as it is sterile is no infection from cleaning bottles, etc.
Causes the uterus to contract and helps the mother recover quickly.
May also help reduce the chance of breast cancer in the mother.
Milk production is stimulated by prolactin and lasts until the infant quits nursing.
Birth Control
Organic Contraception
monitoring mucus and body temperature to avoid having intercourse during ovulation.
Synthetic Contraception
Many techniques exist, including surgical, chemical, and mechanical ones.
1. Sperm are blocked by caps, diaphragms, and condoms.
2. Ovulation-blocking hormones and spermicides to destroy sperm.
3. Fallopian tubes or sperm duct tying tubes.





Comments