Leaving cert Biology Revision: Breathing System
- Javeria Saleem
- Jun 25, 2024
- 1 min read
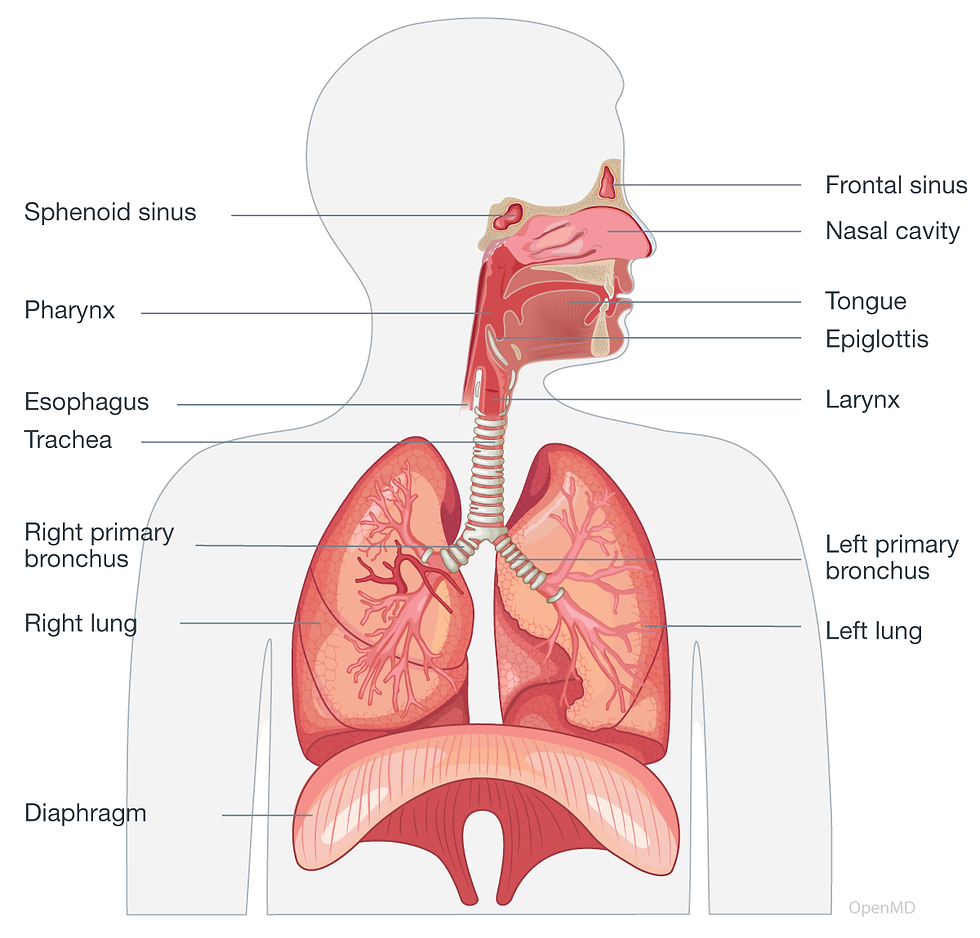
When our cells use food for energy in a process called cellular respiration, they need oxygen. As they break down the food, they release energy and produce carbon dioxide as a waste product.
The physical process of bringing oxygen into our bodies and releasing carbon dioxide is called breathing.
Oxygen gets into the body of an organism from the air or water around it.
Lungs have:
Lots of space for air and blood to meet.
A good blood supply to carry gases.
Thin walls so gases can move in and out easily.
Breathing and Gaseous Exchange

Breathing is how we get oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from our bodies.
When we breathe in, air goes into our lungs through our nose or mouth. Inside our lungs are tiny air sacs called alveoli. Oxygen from the air goes into our blood and travels all over our body to give us energy.
Carbon dioxide, which our cells make, goes from our blood into the alveoli. Then, when we breathe out, we push the carbon dioxide out of our bodies.
This process is called gaseous exchange. It helps us stay alive by giving our cells the oxygen they need and getting rid of waste carbon dioxide.
Cell structure

Cell structure is how a cell is organized inside. It's like the layout of a house, with different rooms and furniture serving specific purposes.
In a cell, there are parts called organelles, like the nucleus (which holds the cell's instructions), cytoplasm (a jelly-like substance), and cell membrane (like a skin that holds everything together).
Each organelle has a job to do, like making energy, building proteins, or storing information.





Comments